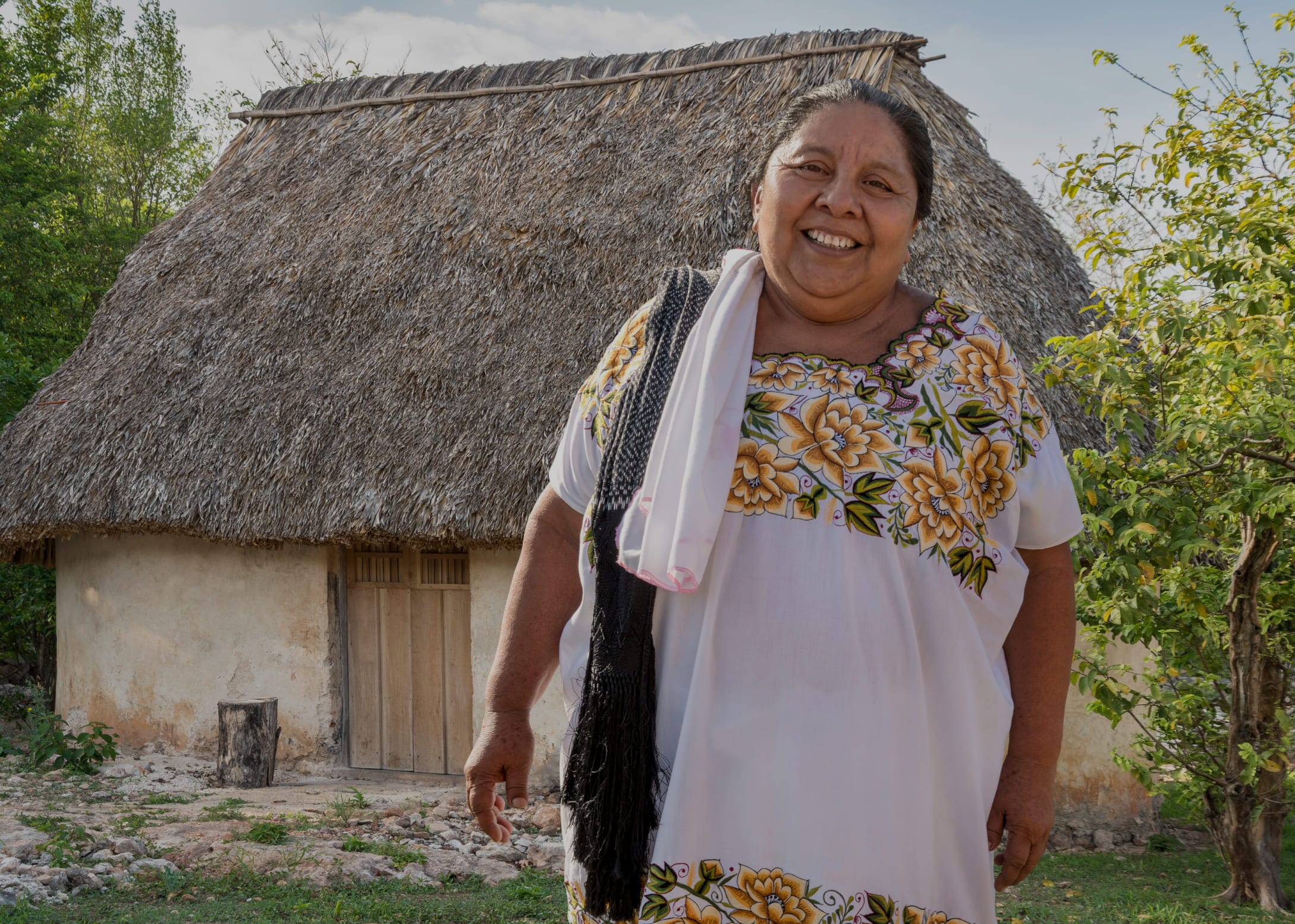IMPACT
Innovation for the environment
Deforestation of mangroves, forests and jungles causes 20% of total greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere.
Deforestation of mangroves, forests and jungles causes 20% of total greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere.
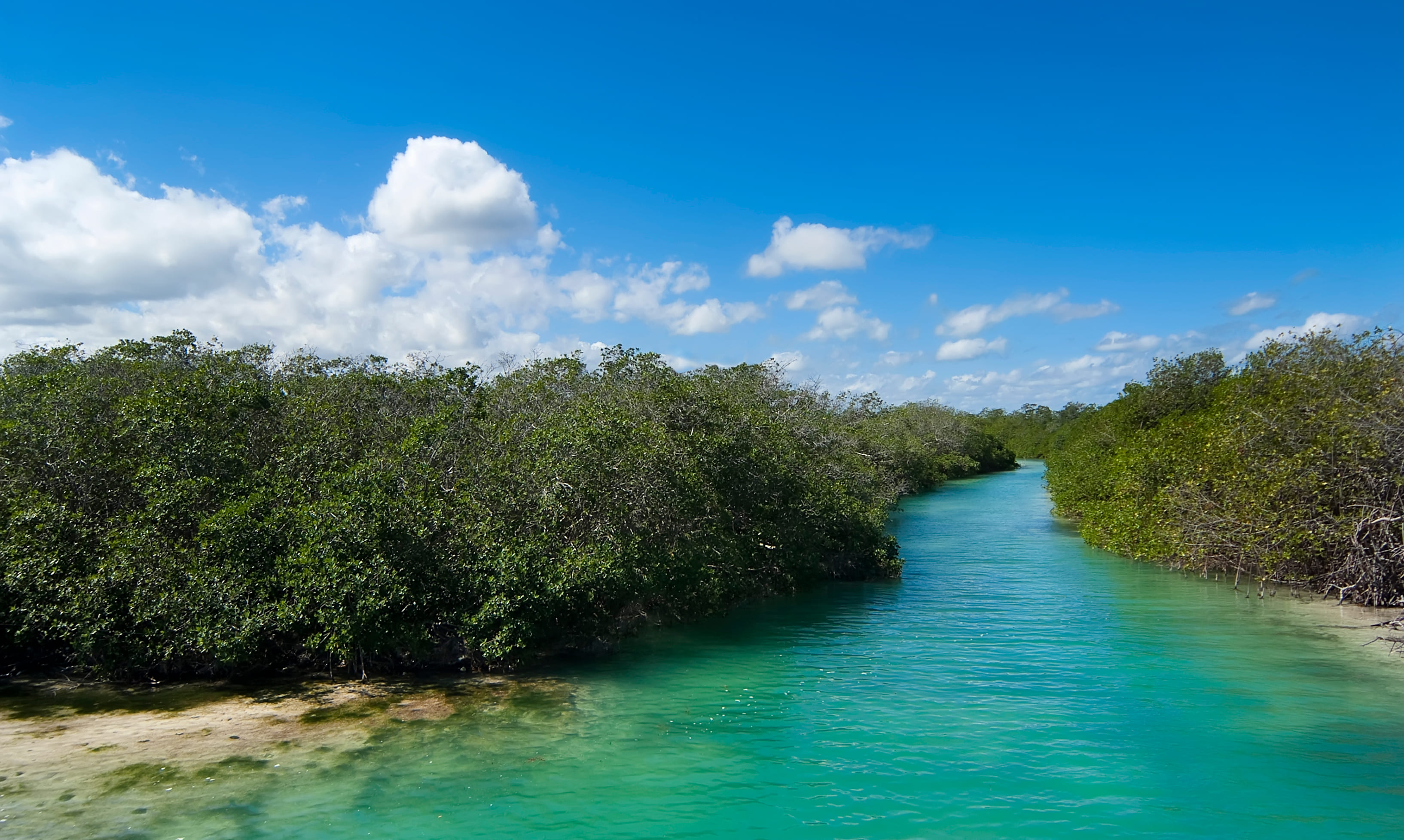
Mangroves are the ecosystem that captures these gases the most and therefore combats climate change the most.
The Chaac Project is aligned with the UN Sustainable Development Goals and in particular with Climate Action (13)

Shared Prosperity Shared Prosperity
Our proposal is to drive long-term sustainable development with people and their communities at the center
The central focus in the communities translates into the following actions:
-
Knowledge and respect for the customs and rights of communities
-
Identification of all stakeholders, ensuring their full and effective participation
-
Obtaining free, prior and informed consent
-
Analysis and monitoring of direct and indirect costs, benefits and risks
-
Identification and constant maintenance of high conservation values
-
Demonstration of net positive benefits in terms of climate, community and biodiversity
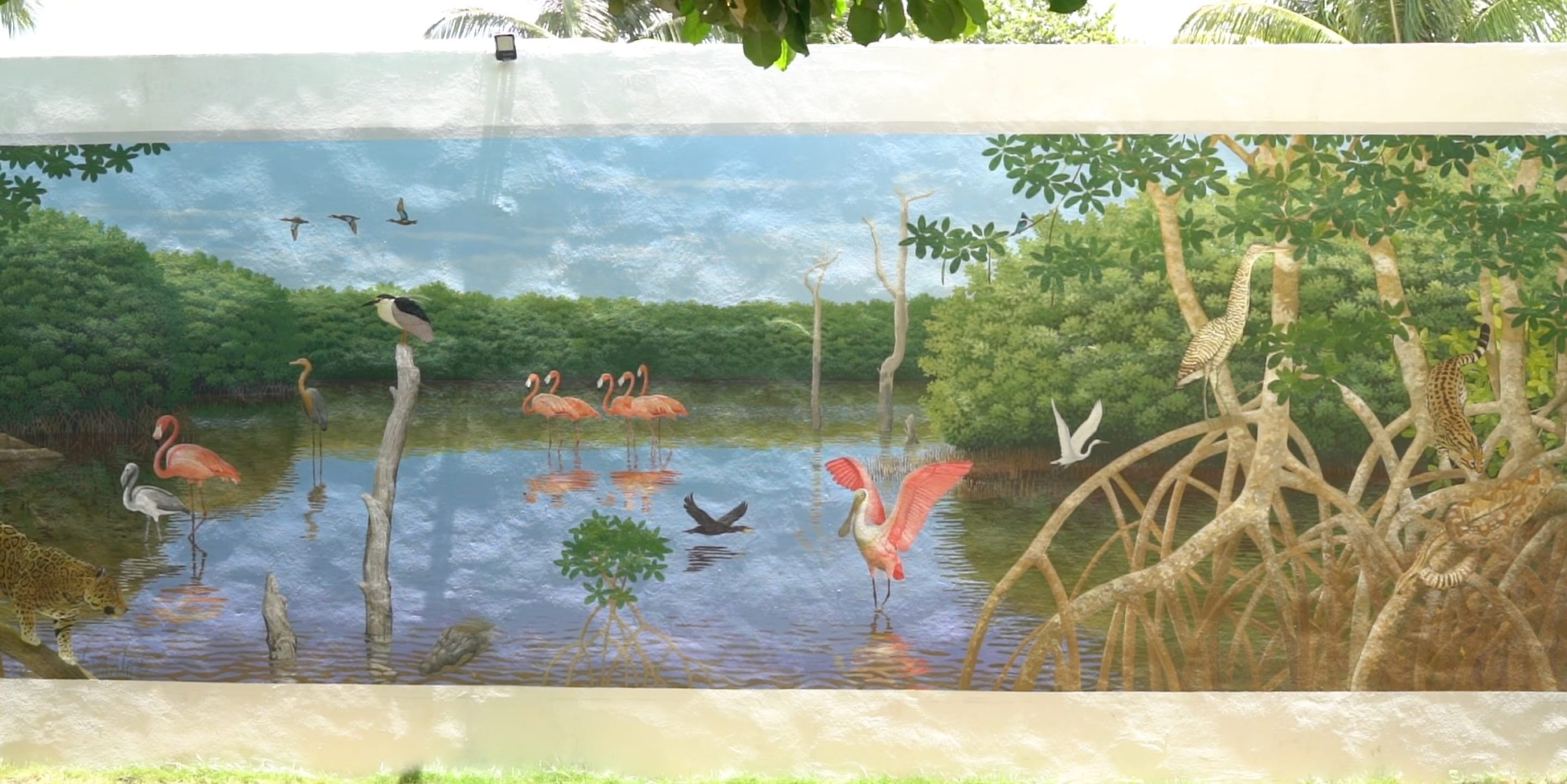

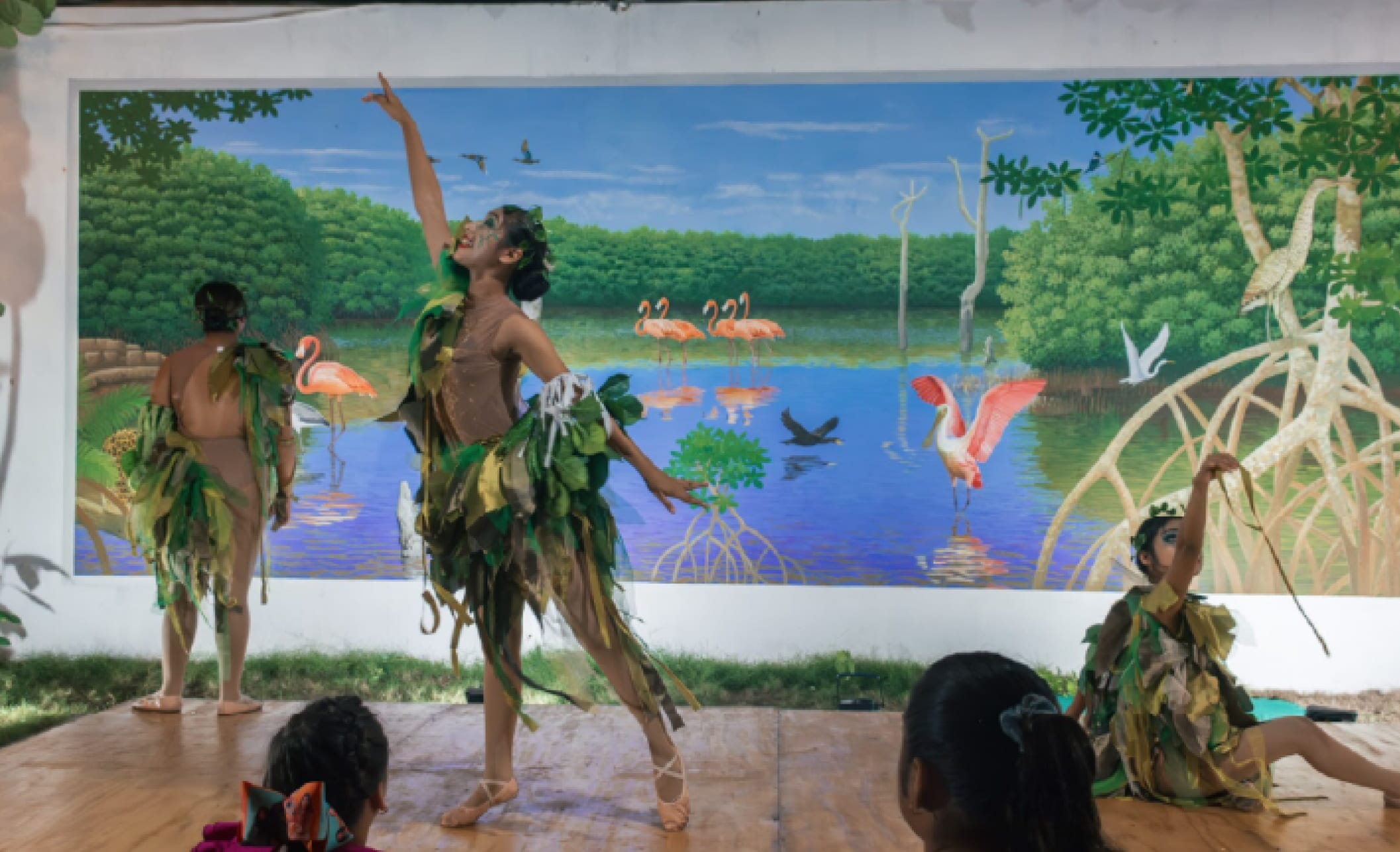
Image of the mural created by Yucatecan artist David Mex during the Chaac Project activities
Life in the mangrove
This work was curated by Mexican artist Alonso Gorozpe, internationally recognized for his artistic, social, and community work.
The work was developed within the context of the Chaac Project’s activities, with social engagement art being an essential tool for putting communities at the center.
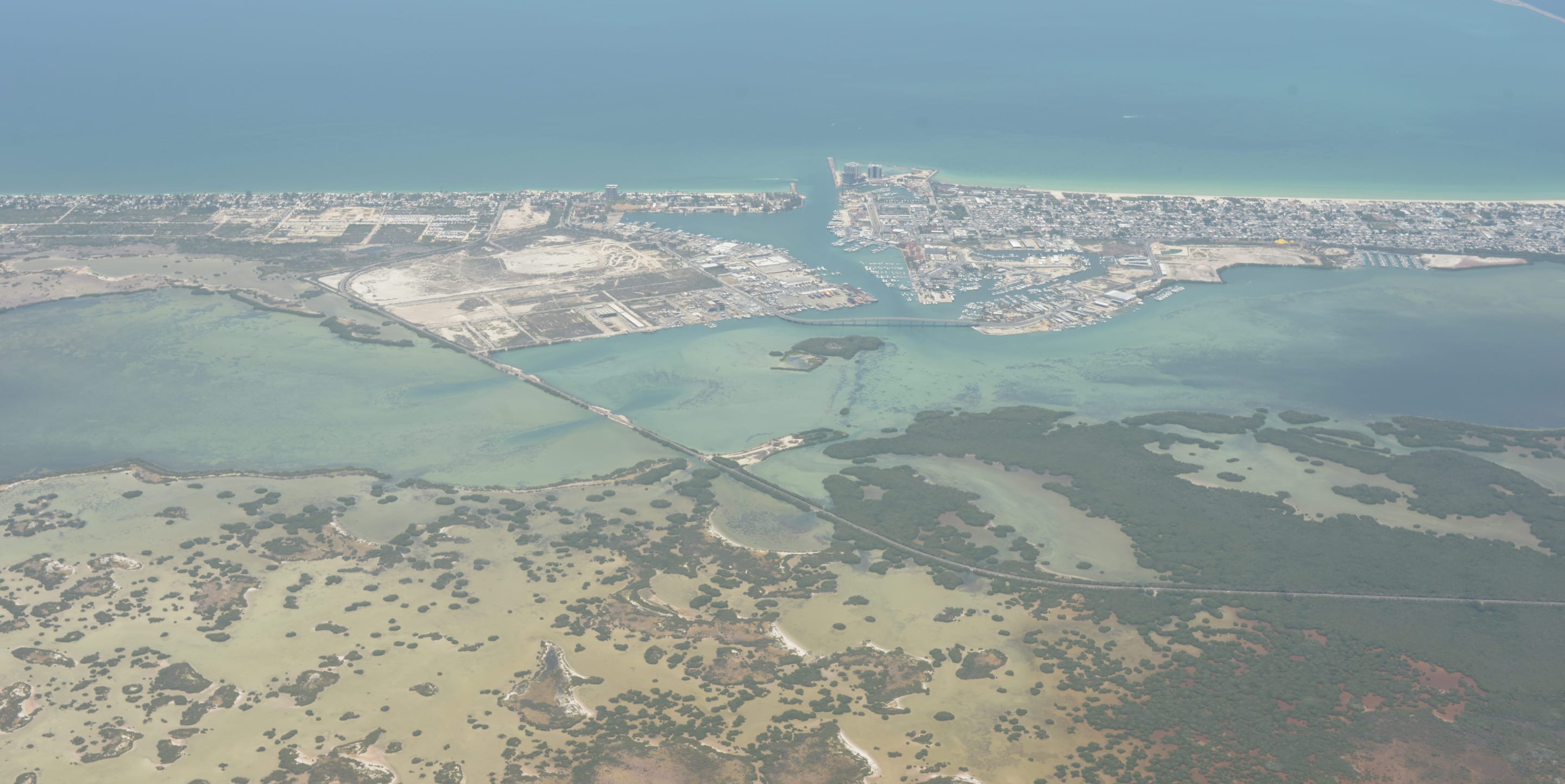
The mangroves of Yucatan provide sustenance to communities
Understanding this, the Chaac Project aligns with the UN Sustainable Development Goal (8) of decent work and economic growth
Mangroves have great socioeconomic value and, therefore, the benefits and opportunities that the Chaac Project will enhance will be implemented in a participatory manner.

Our live progress Our live progress
Global examples
Combating climate change requires comprehensive, large-scale solutions, which is why we were inspired by the model implemented in the Indus River Delta in Pakistan, which achieved the protection and restoration of 100,000 hectares.